
METAL ION BONDING FREE
Solids bonded with ionic bonds have crystalline structures and low electrical conductivity, which is due to lack of free moving electrons. These stable bonds are also called electrostatic bonds. When these ions are brought together, the attraction forces are occurred due to opposite charges of ions. Atoms with very few electrons in their outermost shell tend to donate the electrons and become positively charged ions, while atoms with more electrons in their outermost orbit have a tendency to receive electrons and become positively charged ions.

What is the difference between Ionic Covalent and Metallic Bonds? What are Ionic BondsĬertain atoms tend to donate or receive electrons in order to become more stable by completely occupying their outermost orbit. The main difference between ionic covalent and metallic bonds is their formation ionic bonds form when one atom provides electrons to another atom whereas covalent bonds form when two atom shares their valence electrons and metallic bonds form when a variable number of atoms share a variable number of electrons in a metal lattice.Ĥ. Primary bonds have relatively high bond energies and are more stable when compared with secondary forces. Secondary bonds include dispersion bonds, dipole bonds, and hydrogen bonds. There are three types of primary bonds namely ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds.
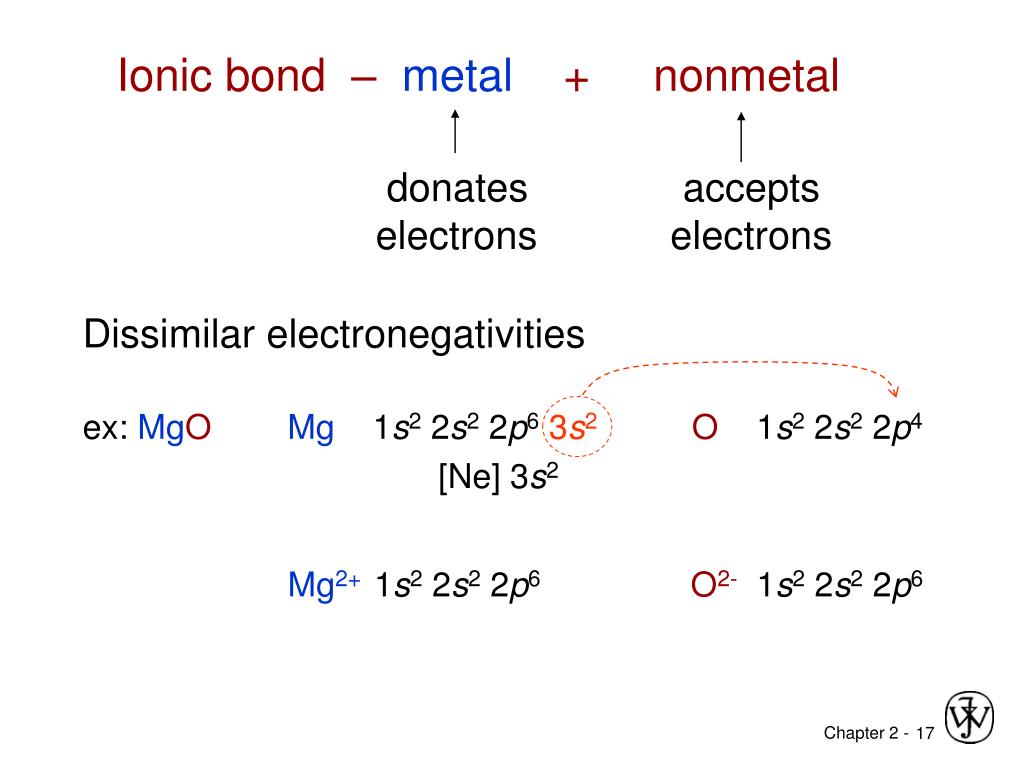
Primary bonds are the chemical bonds that hold atoms in molecules, whereas secondary bonds are the forces that hold molecules together. Main Difference – Ionic vs Covalent vs Metallic Bondsīonds can be divided into two broad categories primary bonds and secondary bonds.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
